A network administrator is responsible for maintaining and improving the performance of an organization’s computer network. They develop, implement and manage the layout or topology of each network to enhance its function. If you work as a network administrator or are pursuing a career in this field, then you might be interested in learning about different network topology types. In this article, we explain what network topology is, list seven types of configurations and discuss the key features of network topology to help you choose the right setup for different circumstances.
Recommended
What is network topology?
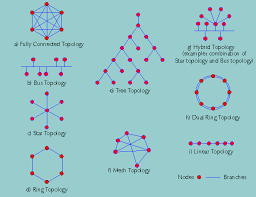
Network topology refers to the way different computers, devices or nodes connect to each other in a communication network. It describes their physical arrangement and explains the logical flow of information throughout the network. A computer network topology can consist of one physical topology and several logical topologies.
A physical topology explains how computers, devices or nodes connect with each other in a network based on their location. It involves assessing the physical layout of network cables and workstations. Conversely, a logical topology explains how data flows from one device to another based on network protocols. It assesses the way devices communicate with each other internally. Therefore, network topology defines the virtual shape, layout and structure of a network from both a physical and logical viewpoint.
7 network topology types
There are seven primary network topology types. Which one you choose to use may depend on an organization’s size and specific needs. Here’s an overview of each of these seven network topology types to help you get started:
1. Point-to-point network topology
Point-to-point network topology is the simplest method. This type of network topology involves connecting two nodes or devices using a common link. The two devices could be two computers, servers, routers or switches connected to each other with a cable. Point-to-point network topology is common in computer networking, computer architecture and telecommunications systems. Some of the advantages of using point-to-point network topology include:
-
High bandwidth and speed
-
Low latency
-
Easy maintenance
2. Bus network topology
Bus network topology is a foundational method that many network administrators use to connect all of the devices or nodes to one primary cable with various drop lines and taps. Drop lines are the cables that connect to the primary cable, also known as the bus, while taps are the individual connectors. This creates one channel for communication throughout the network. When someone uses their computer to send a message through this type of network, all of the connected computers are aware of this action.
However, only the receiver of the message can accept it by verifying its address, which is attached to the data frame. The rest of the computers in the bus network topology reject the message automatically. Once the message reaches its destination, a terminator removes this data from the communication line to prevent data flow disruption and signal bounce. This setup is often an excellent option for small networks because each computer in the network works independently while having access to the network’s full capabilities. Using bus network topology offers the following benefits:
-
Easy installation and implementation
-
Minimal cabling
-
Cost efficiency
3. Ring network topology
Ring network topology consists of two primary point-to-point links that connect one device to two more devices located on each side of it. This creates a ring of devices that data can flow through until it reaches its target device. In this configuration, the way messages pass from one device to another is circular and unidirectional. Each device or computer in the ring has access to the message for a fixed amount of time to assist with the transmission. When the message reaches its destination, the receiver removes the data. Some of the advantages of using ring network topology include:
-
Easy installation
-
Minimal cabling required
-
Reduced data collision
4. Star network topology
Star network topology is the most common configuration. In this layout, each device or node connects to a central network hub. Devices use this central hub to communicate with each other indirectly. If a device wants to send or receive a message, it must first contact the hub to act as a middleware between devices. Once the hub understands what type of message the device wants to send, it transmits it via broadcast or unicast to the designated receivers.
To establish star network topology, network administrators connect each device to the hub using one input-output port and one cable. The main reason Star network topology is so popular is because it improves network security by preventing data from passing through every device. Some of the other advantages of using star network topology include:
-
Centralized control
-
Easy scalability and reconfiguration
-
Cost-efficiency
5. Mesh network topology
Mesh network topology involves creating a dedicated point-to-point link between each device in a network. This allows data to transmit directly between two devices without flowing through other devices in the same network. There are two primary types of mesh network topologies. The first is a full mesh network topology. In this configuration, each node connects to every other node within the network.
The second is a partial mesh network topology. In this layout, some of the nodes may not be connected to every single node within the network. The links between nodes in both types of mesh network topologies are typically simple links, which means the data only moves in one direction. However, some network administrators may replace two simplex links with duplex links to allow data to flow between two nodes in both directions simultaneously. Some of the advantages of using mesh network topology include:
-
Fast communication
-
More privacy and better security
-
Decreased congestion on channels
6. Tree network topology
Tree network topology connects star networks by integrating bus networks to create a parent-child hierarchy. In this configuration, each node is either directly or indirectly connected to the primary bus cable. In order to accomplish this, network administrators divide the network into segments, which makes them easier to maintain. Each segment consists of a primary hub that connects all of the sub-hubs. Some of the advantages of using tree network topology include:
-
Extended distance network coverage
-
Limited data loss
-
Increased number of direct and indirect nodes
7. Hybrid network topology
Hybrid network topology combines at least two other network topologies. This type of configuration is popular because it allows network administrators to create network topologies that are practical and meet the unique needs of each organization. For example, a network administrator might use a bus network topology to house both a star network topology and a ring network topology by using drop lines and taps to connect with them.
This makes it easy for network administrators to select the best features of each type of network topology. It also allows them to customize network topologies for different departments within an organization to improve the flow of data and increase security as needed. Some of the advantages of using hybrid network topology include:
-
Increased volume of nodes
-
Improved flexibility
-
Increased reliability
Key features of network topology
Choosing the right network topology can improve data efficiency, reduce operational costs and optimize resource allocation. Understanding what features to focus on when comparing different network topology types can help you make an informed decision. Here are some of the key features of network topology that may vary depending on the configuration you select:
-
Nodes: In networking, nodes refer to connection points, redistribution points and communication endpoints.
-
Cables: The physical network topology consists of several types of cables and equipment, including coaxial cables, twisted pair cables and optical fiber cables.
-
Hub and switch: The hub and switch connect multiple devices in a network, receive messages and transmit them to the correct nodes or devices.
-
Router: A router analyzes, receives and transmits information between different IP networks by identifying the correct IP addresses of source and destination hosts.
I hope you find this article helpful.