Fixed costs are business expenses that don’t change relative to the production output of a company, and there are many types of fixed costs that can affect how a company operates. One of these types is discretionary fixed costs, which are nonessential costs that companies can often eliminate when needed. If you’re interested in learning about some different strategies companies use to structure their finances, you might want to learn about discretionary fixed costs. In this article, we define this term, provide eight discretionary fixed-cost examples, and review why they’re important.
What are discretionary fixed costs?
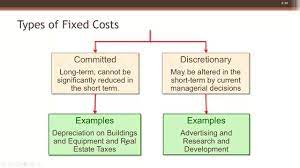
Discretionary fixed costs are a type of fixed cost that a company can eliminate from its budget without a major impact on its normal operations. To understand how these expenses work, it can be helpful to identify the difference between fixed and variable costs. A company’s variable costs change based on how many products it creates, because these costs typically come from the materials required for each unit produced. Fixed costs are expenses like rent and property taxes that a company has to pay, regardless of how many units it produces.
Within the category of fixed costs, there are many variations. Discretionary costs are non-essential expenses that aren’t controlled by the amount of products produced. Companies take on discretionary fixed costs as ways to grow the business or expand market shares. Because discretionary fixed costs aren’t essential to the business’s normal operations, it can take on discretionary fixed costs as part of its development strategy.
8 discretionary fixed cost examples
Here are eight discretionary fixed-cost examples:
1. Advertising costs
Advertising budgets are one of the most common types of discretionary fixed costs. While a company might not need to advertise to sell its products, effective advertising campaigns can greatly improve the profitability of a business. Because the number of units that a company produces doesn’t affect the cost of advertising, these expenses are fixed costs.
Ad campaigns are discretionary because these expenses aren’t essential for a business to operate. The amount of money that a company spends on advertising is usually based on the discretion of its executive officers or accountants. While spending money on advertising campaigns can be an effective way to promote a product, a company that needs to reduce costs might eliminate its advertising budget before cutting back on essential services.
2. Public relations expenses
Most large companies have a budget set aside for managing public relations. Maintaining a positive relationship with the public can help companies expand by influencing consumer decisions. Companies that promote the positive impacts the company has on society often enjoy increased patronage from conscious consumers.
While managing public relations is important for companies that want to be viewed favorably by potential customers, these costs are discretionary because they don’t impact the core function of the business. Similar to ad campaigns, public relations expenses provide a way for businesses to promote themselves, but if revenue is down, then the executives might choose to stop spending money on public relations costs.
3. Employee training
Training programs are a common discretionary cost that companies might choose to eliminate once they’re no longer necessary. When hiring new employees or creating a new team, providing in-depth training can be a good way to increase morale while also providing everyone with the tools they need to succeed. Expensive training programs can be beneficial, but once they’re no longer needed, companies might choose to reduce the funding for them. Because training programs are not always vital to the core function of a business, they’re often considered discretionary fixed costs.
4. Research and development
Developing new products can be an effective way to grow a business, but once the business has a wide range of products, spending more money on development might not be worthwhile. Research and development can be important, but the costs associated with these programs are discretionary, since they aren’t essential to the business’s normal operations. Companies might choose to spend money on research programs until they meet the goals of the program and then direct the funding to new projects afterward. Shifting money between development and advertising can be an effective strategy to create new products while staying under budget.
5. Charitable donations
Donating to charity can be a good strategy for companies that want to give back to their community. Charitable donations can also provide tax benefits that increase long-term profitability. While donating to charity is a commendable activity, companies that are struggling financially might not have enough revenue to spare on donations, making it discretionary. Cutting back on charitable donations can help a company stay under budget after a difficult quarter.
6. Software licenses
Licensing software can help increase the efficiency of a company’s employees or provide helpful systems for managing the business. While these types of software provide a wide range of benefits, the licensing fees are a type of discretionary cost. Paying for programs can help a company manage its operations, but if the business needs to cut back on spending, then it might choose to remove these licenses until it can meet its revenue goals again.
7. Partnerships with contractors
If a business needs extra help with a project, it might choose to work with a contractor team rather than hire more employees. Working with contractors can be a good way for companies to finish projects without taking on the full cost of hiring a new team. These contractor partnerships are discretionary expenses because, while they may be helpful in the short term, they’re not usually necessary for the business to continue operating.
8. Employee benefits
Employee benefits, such as vacation time, insurance plans, and bonuses, are another type of discretionary fixed cost. These benefits can be an effective way for a business to increase employee satisfaction and retention, but if it needs to save money, then a company might remove them. While providing competitive benefits can be a good way to increase morale, companies that need to reduce spending might target these costs before removing essential services if it means it can keep its employees on the payroll.
Why are discretionary fixed costs important?
Discretionary fixed costs are important because they provide outlets for excess revenue that can help grow the company or improve employee satisfaction. Companies that have a lot of discretionary fixed costs are also usually more durable in financial downturns. Because these types of businesses have expenses they can remove without affecting their core functions, they’re able to easily streamline the budget without having to rely on cutting back on essential services or employee positions. Discretionary fixed costs can also provide a financial buffer that can reduce the impact of unproductive quarters or negative changes in the market.
I hope you find this article helpful.
Leave a Reply