Distribution marketing is a key consideration for marketers, as it helps businesses connect products and services to consumers. Creating this connection helps companies achieve marketing goals such as raising brand awareness and increasing profits. Understanding distribution marketing and distribution channels helps marketers select the best options for their business. In this article, we explain what distribution marketing is and list some proven distribution channels.
Recommended
What is distribution marketing?
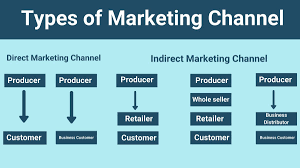
Distribution marketing is the way firms make their products and services available to consumers. Distribution in marketing is an element of the “place” category in the four P’s of marketing. When many marketers consider place, they focus on where they promote products and services. However, they must also consider where customers make their final purchase decisions.
Eight effective distribution channels
With the rise of online shopping, marketers have more choices about where to shop than ever before. These are distribution channels. Marketers may choose a single distribution channel or several different channels. Here are eight distribution channels that can help consumers access products:
1. Direct sales
Companies can sell products and services directly to customers through their own stores, websites or merchant marketplaces. This arrangement works well for businesses such as bakeries, who make products in the same location they sell them. Digital products, such as audio files and software, also suit direct distribution. For example, an independent record label may let fans purchase and download music directly from its website. Some benefits of direct sales include:
-
Increased trust: Customers may feel closer to the business as they know the company wants to deal with them directly.
-
Greater control over customer experience: Direct sales lets businesses control all facets of product distribution and customer experience. As customers deal directly with the supplier at all times, the direct sales process helps solve these issues more efficiently.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Businesses save the money they might spend on services from third-party distributors or sellers. They can therefore lower their prices to gain a competitive advantage.
2. Retailer
A retailer is one of the most popular and effective distribution channels. Retailers include supermarkets, department stores, specialty stores and big-box retailers. Today marketers working with retailers can put their products in physical stores, online stores or both. Some benefits of using a retailer include:
-
Product interaction: When consumers buy from brick-and-mortar retailers, they can interact with products before buying them. Being able to see how items look in person and even test them out gives consumers confidence.
-
Increased product awareness: Retailers can introduce consumers to products they didn’t know about before browsing.
-
Diverse promotion strategies: Marketers can work with retailers on strategic placement, product demonstrations and promotional materials to make their products more appealing.
-
Increased audience: People are often loyal to retailers. Companies selling their products through retailers can leverage the loyalty consumers already feel towards these outlets.
3. Independent distributor
Independent distributors are agents who supply products to retailers. Distributors are typically used as a link in the marketing distribution chain. Some benefits of using an independent distributor include:
-
Established networks: Distributors have established networks of retailers they can encourage to purchase products. Distributors use these connections to put products in front of the most receptive consumers.
-
Easier storage: Distributors store products at their own warehouses, saving businesses the expense of maintaining their own storage facilities.
-
Motivation to work for the business: As distributors buy products and store them in their own warehouses, they are usually motivated to sell them on.
4. Reseller
Resellers are very similar to distributors, but they supply directly to customers rather than retailers. Rather than purchasing and storing products as distributors do, resellers usually have online stores. They take commissions of the price on every sale. They then organize for products to ship from the manufacturer or supplier directly to the customer. Some benefits of using resellers include:
-
Cost-effectiveness: Resellers are more affordable than distributors as they do less work promoting products.
-
Increased visibility: A business’s products may be more visible after partnering with a prominent reseller. For example, an independent musician may use a well-known reseller to distribute a new album and gain a wider audience.
-
Value-added services: Some resellers offer additional incentives to shoppers that can make products more appealing. One example of distribution with value-added services is a software reseller offering customer support and training programs.
5. Wholesaler
Wholesalers buy and sell goods in bulk. Wholesalers can be a link in the marketing distribution chain, selling their products to retail stores. However, some wholesalers also sell directly to the public through large open warehouses and online stores. If your products suit bulk sales, as many grocery items do, you might consider distributing through a wholesaler. Some benefits of using wholesalers include:
-
Low costs that entice buyers: Since they work with such large quantities, they can often sell products at a much lower cost than retailers.
-
Efficiency: Since wholesalers buy and sell in bulk, they can help businesses move their products efficiently.
-
Industry knowledge and connections: Businesses can leverage their strong supply knowledge and industry connections.
6. Intensive distribution
Intensive distribution involves selling products through a large number of different channels. This marketing distribution approach is commonly seen with inexpensive, well-known products, such as soft drinks. People know they can find these products at most supermarkets, convenience stores, eateries and vending machines. Some benefits of using intensive distribution include:
-
Increased reach: Selling in a variety of locations helps businesses enjoy a much wider reach than selling through a single retail chain.
-
Increased trust: Consumers become comfortable with products they see regularly. Since intensive distribution puts products in front of consumers regularly, it can be a great way to build trust.
-
Substitution benefit: By being readily available, companies can often sell their products to consumers searching for similar products that are less accessible.
7. Exclusive distribution
An exclusive distribution deal sees products and services are only available from a single third-party distribution channel. While intensive distribution benefits affordable products, exclusive distribution is a common option for luxury goods. Some benefits of using exclusive distribution include:
-
Exclusivity: Exclusive distribution deals can make products feel more prestigious, which increases interest. For example, some luxury accessories are only available through a single distributor in each international market.
-
Greater control: Businesses have more control over product distribution when dealing with a single channel. They can create strict guidelines for the third-party distributor so their customers have the best experience.
-
Better terms: Distributors want exclusive deals, so they are more likely to negotiate better terms with companies offering these contracts.
8. Selective distribution
Selective distribution provides a middle-ground between intensive and exclusive distribution. Companies favoring selective distribution hand-pick several distribution outlets. For example, a premium accessories brand using selective distribution may trust its accessories to high-end department stores but avoid big-box stores. Some benefits of using exclusive distribution include:
-
Some degree of control: Dealing with a limited number of distribution channels helps businesses control many elements of the sales process, such as how product displays and sales pitches. These controls ensure customers have a consistent experience, no matter where they shop.
-
An element of prestige: Consumers feel products are more special and prestigious when they are not available everywhere.
-
Increased reach: Selective distribution puts products in front of more consumers than exclusive distribution.